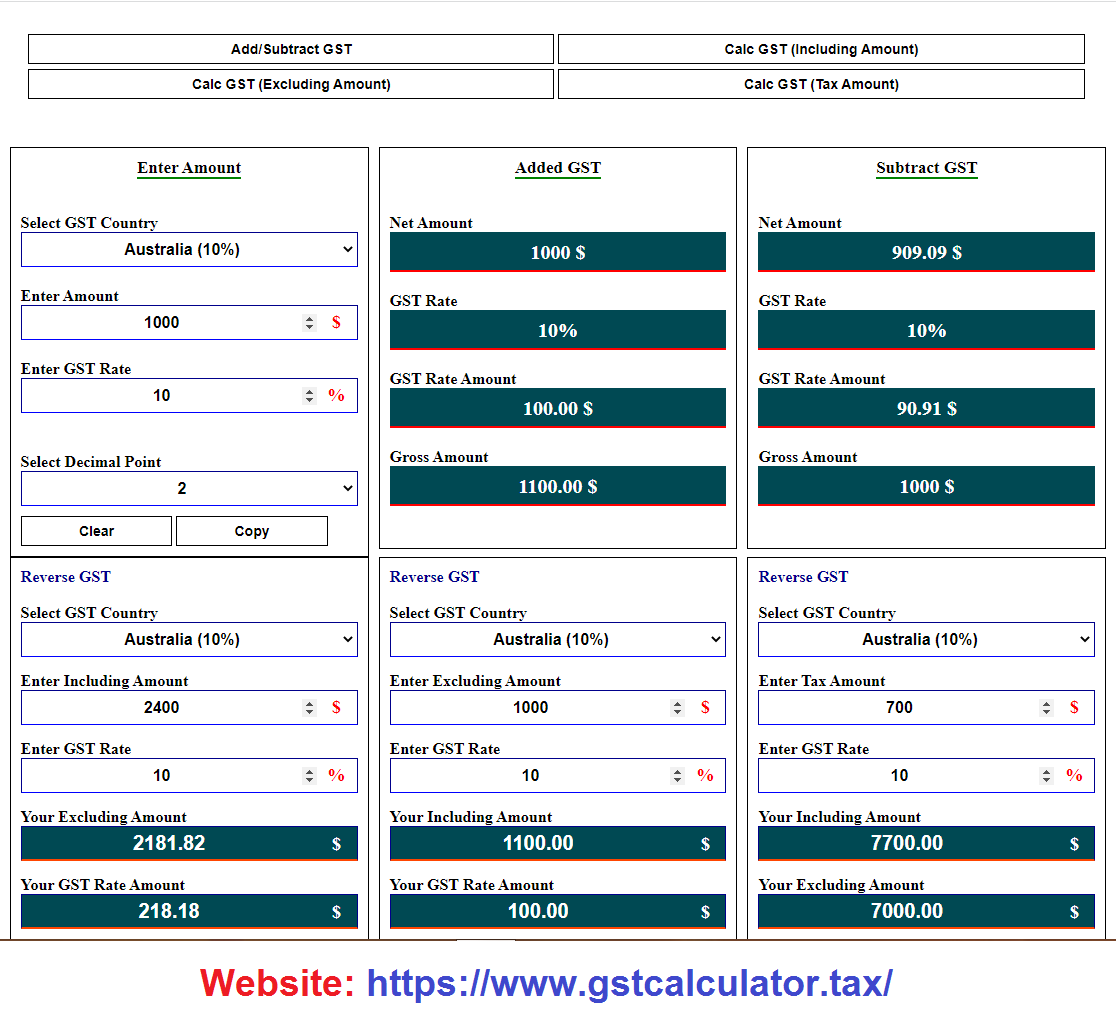
How to Calculate GST in Australia
Goods and Services Tax in Australia refers to a value-added tax levied at a rate of 10% on nearly all goods and services supplied within the country. Calculating GST involves either adding a net amount with the 10% arriving at the price that is inclusive, or deducting the tax from the total to find the price excluding the GST. For example, if the net price is $100 and it already has to include GST, then that would be a total of $110. If the price given already includes GST, one would just need to divide it by 1.1 to obtain the amount before adding GST. Use this tool for Australian GST Calculation GST Calculator. This simple method ensures the accuracy of financial reports and complies with the requirements set by the Australian Taxation Office for businesses and consumers.
How to Add GST in Australia with a Formula
Adding GST to the selling price of a product or service in Australia is as easy as this formula: Original Price x 1.1 = GST-Inclusive Price. Here, the price of 1.1 includes the range of GST at a rate of 10%, which makes it easy for businesses to come up with any final prices with tax inclusions. If the pre-GST cost is $150, then this product's price is multiplied by 1.1, yielding $165, its GST-inclusive amount. This calculation would help make sure that the pricing of goods and services provided to the consumers is clear and GST-inclusive in nature.
How to Remove GST in Australia with Formula
If the price inclusive of GST has to be ascertained, then the exclusive price of GST is arrived at by dividing the total amount by 1.1. That formula removes the 10% part of GST from the given price, showing the price before tax. As an example, if something was priced at $220, including GST, one would divide this figure by 1.1 and get $200 before the GST. This will be helpful for business enterprises or consumers who may want to calculate the amount for GST on the transaction.
Goods and services tax (Australia)
Goods and Services Tax is a broad consumption tax of 10% on most goods, services, and other items sold or consumed in Australia. Australian Goods and Service Tax was initiated in the year 2000 and is managed by the Australian Taxation Office. Being one of the prominent tax revenues, it helps to finance many public services and infrastructures. Certain goods, such as fresh food, healthcare, and educational services, are zero-rated or GST-free to take the burden off essentials. Every business making more than $75,000 annually needs to register for GST, charge it on sales, and make periodic returns in order to create a uniform and transparent taxation system across the sectors. More About GST Goods and services tax (Australia).
GST Rates in Australia
The flat GST rate of 10% percent charged on most goods and services supplied in or connected with Australia, since the GST inception in the year 2000 at a relatively low level compared to other countries' GST/VAT, has had the effect of ensuring that such a tax remains reasonably affordable for most consumers while raising substantial revenue for the government. Others are exempt or GST-free, such as basic food, healthcare, and education, to ease the burden of tax on basic necessities. The single, consistent rate of 10% would simplify GST for both businesses and consumers, creating clarity and ease for businesses in relation to tax obligations overseen by the Australian Taxation Office.